代码示例
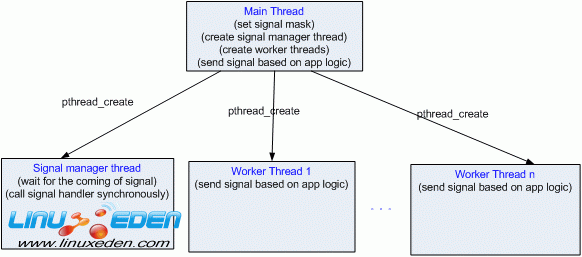
以下为一个完整的在指定的线程中以同步的方式处理异步信号的程序。
主线程设置信号掩码阻碍 SIGUSR1 和 SIGRTMIN 两个信号,然后创建信号处理线程sigmgr_thread()和五个工作线程 worker_thread()。主线程每隔10秒调用 kill() 对本进程发送 SIGUSR1 和 SIGTRMIN 信号。信号处理线程 sigmgr_thread()在接收到信号时会调用信号处理函数 sig_handler()。
程序编译:gcc -o signal_sync signal_sync.c -lpthread
程序执行:./signal_sync
从程序执行输出结果可以看到主线程发出的所有信号都被指定的信号处理线程接收到,并以同步的方式处理。
清单 2. signal_sync.c
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
static int j = 0;
static int k = 0;
pthread_t sig_ppid = pthread_self();
// used to show which thread the signal is handled in.
if (signum == SIGUSR1) {
printf("thread %d, receive SIGUSR1 No. %d\n", sig_ppid, j);
j++;
//SIGRTMIN should not be considered constants from userland,
//there is compile error when use switch case
} else if (signum == SIGRTMIN) {
printf("thread %d, receive SIGRTMIN No. %d\n", sig_ppid, k);
k++;
}
}
void* worker_thread()
{
pthread_t ppid = pthread_self();
pthread_detach(ppid);
while (1) {
printf("I'm thread %d, I'm alive\n", ppid);
sleep(10);
}
}
void* sigmgr_thread()
{
sigset_t waitset, oset;
siginfo_t info;
int rc;
pthread_t ppid = pthread_self();
pthread_detach(ppid);
sigemptyset(&waitset);
sigaddset(&waitset, SIGRTMIN);
sigaddset(&waitset, SIGUSR1);
while (1) {
rc = sigwaitinfo(&waitset, &info);
if (rc != -1) {
printf("sigwaitinfo() fetch the signal - %d\n", rc);
sig_handler(info.si_signo);
} else {
printf("sigwaitinfo() returned err: %d; %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
}
}
}
int main()
{
sigset_t bset, oset;
int i;
pid_t pid = getpid();
pthread_t ppid;
// Block SIGRTMIN and SIGUSR1 which will be handled in
//dedicated thread sigmgr_thread()
// Newly created threads will inherit the pthread mask from its creator
sigemptyset(&bset);
sigaddset(&bset, SIGRTMIN);
sigaddset(&bset, SIGUSR1);
if (pthread_sigmask(SIG_BLOCK, &bset, &oset) != 0)
printf("!! Set pthread mask failed\n");
// Create the dedicated thread sigmgr_thread() which will handle
// SIGUSR1 and SIGRTMIN synchronously
pthread_create(&ppid, NULL, sigmgr_thread, NULL);
// Create 5 worker threads, which will inherit the thread mask of
// the creator main thread
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_create(&ppid, NULL, worker_thread, NULL);
}
// send out 50 SIGUSR1 and SIGRTMIN signals
for (i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
kill(pid, SIGUSR1);
printf("main thread, send SIGUSR1 No. %d\n", i);
kill(pid, SIGRTMIN);
printf("main thread, send SIGRTMIN No. %d\n", i);
sleep(10);
}
exit (0);
}
|
注意事项
在基于 Linux 的多线程应用中,对于因为程序逻辑需要而产生的信号,可考虑使用同步模型进行处理;而对会导致程序运行终止的信号如 SIGSEGV 等,必须按照传统的异步方式使用 signal()、 sigaction()注册信号处理函数进行处理。这两种信号处理模型可根据所处理的信号的不同同时存在一个 Linux 应用中:
- 不要在线程的信号掩码中阻塞不能被忽略处理的两个信号 SIGSTOP 和 SIGKILL。
- 不要在线程的信号掩码中阻塞 SIGFPE、SIGILL、SIGSEGV、SIGBUS。
- 确保 sigwait() 等待的信号集已经被进程中所有的线程阻塞。
- 在主线程或其它工作线程产生信号时,必须调用 kill() 将信号发给整个进程,而不能使用 pthread_kill() 发送某个特定的工作线程,否则信号处理线程无法接收到此信号。
- 因为 sigwait()使用了串行的方式处理信号的到来,为避免信号的处理存在滞后,或是非实时信号被丢失的情况,处理每个信号的代码应尽量简洁、快速,避免调用会产生阻塞的库函数。
小结
在开发 Linux 多线程应用中, 如果因为程序逻辑需要引入信号, 在信号处理后程序仍将继续正常运行。在这种背景下,如果以异步方式处理信号,在编写信号处理函数一定要考虑异步信号处理函数的安全; 同时, 程序中一些库函数可能会被信号中断,错误返回,这时需要考虑对 EINTR 的处理。另一方面,也可考虑使用上文介绍的同步模型处理信号,简化信号处理函数的编写,避免因为信号处理函数执行上下文的不确定性而带来的风险。(责任编辑:A6)
时间:2009-06-19 13:06
来源:developerWorks 中国
作者:周 婷
原文链接
 3G Eden
3G Eden RSS
RSS